Pollution Control
Exhaust gas cooling nozzles
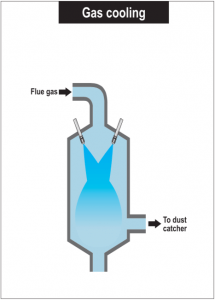
Process
Common issues with Gas Cooling process
- Clinker issue for cooling tower and nozzles
- Risk of corrosion
- Nozzles dripping (excess water)
- Problems caused by dust adhesion to interior walls or around outlet of gas cooling tower
- In an installation where the gas and sprayed water is coming from the top of the tower:
- Unvaporized-water drainage needed from the lower part of the tower due to excess water
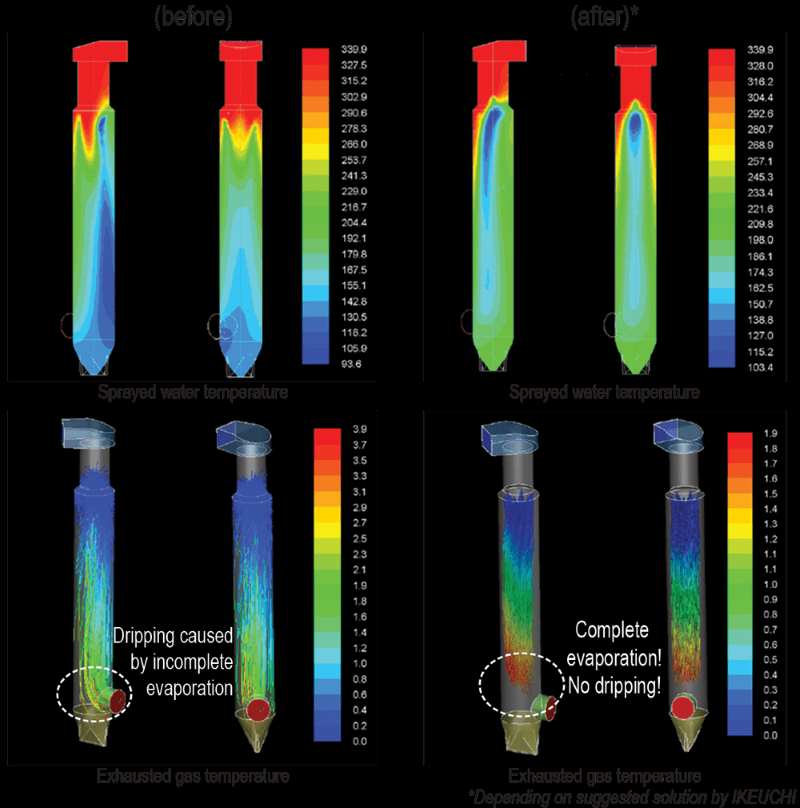
Solution: Innovative Gas Cooling Nozzles
We understand the significance of droplet size and full evaporation in gas cooling towers to ensure maximum cooling effect without extra drainage.
Therefore, we have a wide range of nozzles with different droplet sizes, spray capacities and spray angle to suit every request.
Customers realize lower running costs and minimal maintenance downtime with our clog-resistant nozzles and wide range of material options.
Example of Systems / Products used for gas cooling nozzles
- ASPB series – Air-assisted Spillback Nozzles [NEW]
GSIMII series Fine Fog Pneumatic Spray Nozzles
SPB series Spillback Nozzles
Solutions
Benefits
- Effective cooling with full evaporation
- Minimal maintenance downtime
- Lower running costs
Advantages of the solution
- Clog-resistant nozzles
- Wide range of material options like for anti-corrosion Titanium material, Hastelloy® or other
- Wide range of spray capacity with minimal variation in droplet sizes and excellent atomization
- Energy-saving nozzles with a low consumption of compressed air
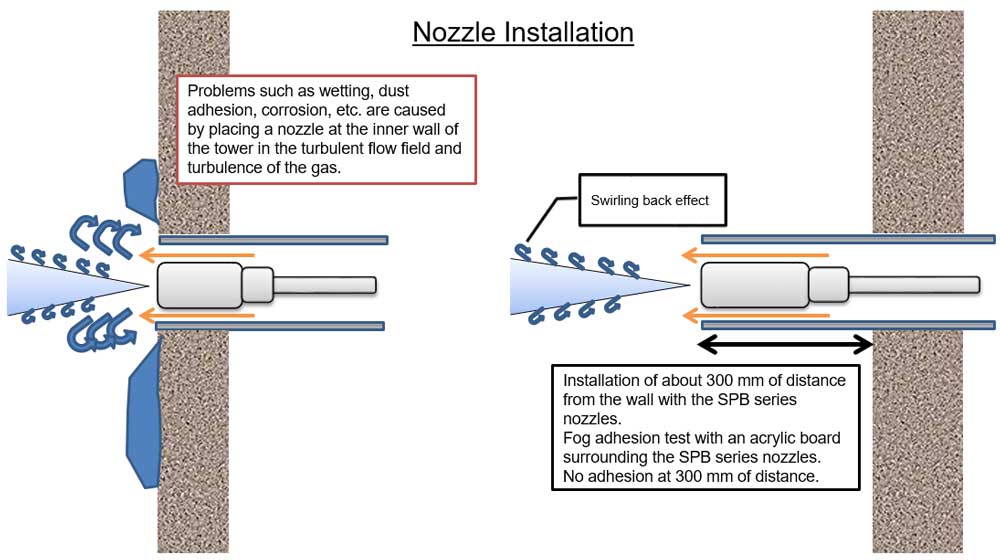
- For an installation of the nozzle horizontally from the side, the high-velocity fog reaches the center of the gas cooling tower without being disturbed by the exhaust gas flow
- Other efficient installation is possible with different angle / positioning of the nozzle based on our recommendation and your plant’s layout
Other applications for these nozzles
- Cooling: Gas, moldings, refractories, incinerators (flue gas desulfurization), cement factories, glass factories, blast furnaces, iron works, blast furnaces (dry dust catcher)
- Moisture control: Flue gas, concrete, paper, cardboard, blast furnaces (water spraying to hot blast stove)
- Combustion: Oil, waste fluid
- Chemical reaction: denitration
- Iron making process: Cooling flue gas before gas turbine, Cooling refractories at maintenance, Dust suppression at casting of pig iron
- Steel making process: Cooling converter shell at maintenance, Flue gas cooling on electric furnace, Dust suppression at casting of steel
- Rolling mill and surface finish process: Cooling flue gas from heating furnace, Dust suppression on rolling mill outlet
